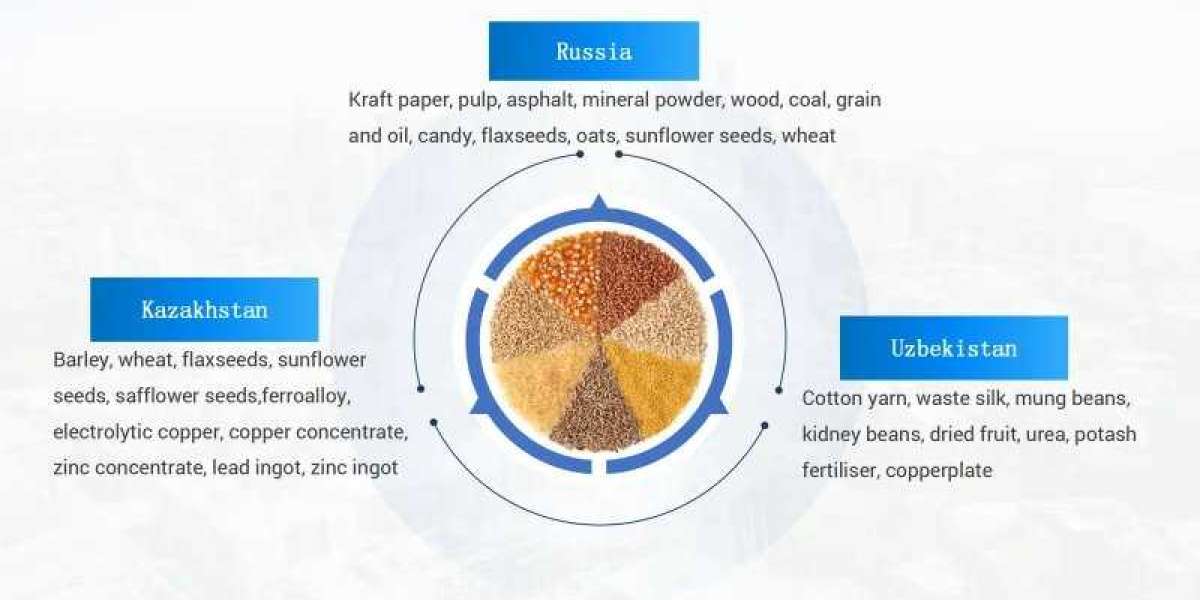
The import and export of agricultural products play a crucial role in meeting global food demands and fostering economic growth. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the transportation of agricultural goods across borders has become a complex and vital process. BENMA LOGISTICS will explores the key features and considerations involved in the import and export transportation of agricultural products, highlighting the measures taken to ensure freshness, quality, and compliance with international standards.
1. Regulatory Framework and Documentation:
The transportation of agricultural products across borders requires adherence to a comprehensive regulatory framework. Import and export permits, phytosanitary certificates, and other documentation are essential to comply with the regulations of both the exporting and importing countries. These documents verify the quality, safety, and origin of the agricultural products, ensuring that they meet the necessary standards and are fit for consumption.
2. Packaging and Labeling:
Proper packaging and labeling are crucial for the successful transportation of agricultural products. Packaging materials should be chosen carefully to protect the goods from damage during transit and maintain their freshness. Additionally, clear and accurate labeling is necessary to provide information about the product's origin, ingredients, nutritional value, and any potential allergens. Meeting packaging and labeling requirements is essential to facilitate customs clearance and ensure consumer safety.
3. Cold Chain Logistics:
Maintaining the freshness and quality of perishable agricultural products during transportation is a top priority. The cold chain logistics system, which involves the controlled temperature management of goods from the point of origin to the final destination, plays a vital role in achieving this objective. Refrigerated containers, temperature-controlled warehouses, and specialized transportation vehicles are employed to preserve the integrity of temperature-sensitive products such as fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meat. Continuous monitoring and strict adherence to temperature requirements are essential to prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.

4. Transportation Modes:
Various transportation modes are utilized in the import and export of agricultural products, depending on factors such as distance, perishability, and cost-efficiency. Sea freight is commonly used for long-distance transportation, especially for bulk shipments. Air freight offers faster delivery times and is preferred for perishable goods or high-value products. Road and rail transportation are utilized for shorter distances or when landlocked regions need access to international markets. Each mode has its advantages and considerations, and choosing the appropriate mode is crucial to ensure timely and efficient delivery.
5. Customs Clearance and Border Control:
Navigating customs clearance and border control procedures is a critical aspect of international agricultural trade. Customs authorities enforce regulations, inspect shipments, and collect duties and taxes. Compliance with import and export regulations, accurate documentation, and transparency in declaring the nature and value of the goods are essential to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, border control measures, such as inspections for pests and diseases, are in place to protect domestic agriculture from potential threats.
6. Quality Control and Traceability:
Maintaining quality control throughout the transportation process is vital to ensure that agricultural products reach consumers in optimal condition. Quality control measures include regular inspections, sampling, and testing to verify compliance with safety and quality standards. Furthermore, establishing traceability systems allows for the identification of the product's journey from farm to fork, enabling swift recalls in case of any safety concerns and enhancing consumer confidence in the supply chain.
7. Market Access and Trade Agreements:
Market access for agricultural products is influenced by trade agreements and regulations between countries. Tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers can significantly impact the import and export of agricultural goods. Trade agreements, such as free trade agreements and regional economic partnerships, aim to reduce trade barriers and facilitate smoother agricultural trade. Understanding the market access conditions and leveraging trade agreements can enhance opportunities for agricultural producers and exporters.
Conclusion:
The import and export transportation of agricultural products involve a range of features and considerations to ensure the freshness, quality, and compliance of goods across borders. From regulatory frameworks and documentation to cold chain logistics, packaging, transportation modes, customs clearance, and quality control, each aspect plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of agricultural trade. By understanding and navigating these complexities, stakeholders in the agricultural industry can contribute to global food security, economic growth, and sustainable development.